How to Create a Multilingual Drupal Site?
Setting up a multilingual website in Drupal opens the door to a global online marketplace, allowing businesses to reach different cultural audiences by presenting content in multiple languages. In this article, we will discuss the process of configuring a multilingual site on Drupal.

Tips for Creating Multilingual Sites on Drupal
Tips for Creating Multilingual Sites on Drupal
There are a few key aspects to remember when creating a multilingual Drupal website. Here are some tips:
- Version – choose a Drupal version that offers support for multiple languages. For example, Drupal 8 and later versions provide built-in tools for multilingual support.
- URL structure – decide how to organize the URLs for different language versions. You can choose between one URL for each language version (e.g. /pl for Polish, /en/ for English) or place the translations on a separate domain/subdomain.
- Content management – make sure your website content is available in different languages. You can translate your Drupal page manually or use automated content translation tools, such as the GTranslate module, which uses the Google Translate API.
- Metatags and SEO – remember to optimize metatags for each language version to improve the website’s visibility.
- Testing – test your website thoroughly to ensure everything works correctly in different language versions. Pay special attention to possible changes in page layout due to differences in word and sentence length between languages to avoid incorrectly displayed content.
Advantages of Creating Multilingual Drupal Websites
Advantages of Creating Multilingual Drupal Websites
There are a few reasons why Drupal is a perfect solution for multilingual websites:
- support for multiple languages – Drupal supports many languages, so you don’t have to install translation modules or extensions. You can simply enable the multilingual feature and start adding new languages,
- translations – Drupal has a management system that allows for website content translation. This includes the user interface, content, and the admin panel,
- easy switching – Drupal includes a language switcher that allows visitors to quickly switch between language versions. You can place it anywhere on the website,
- SEO – Drupal supports SEO-friendly URLs for multilingual sites so that you can set separate URLs for each language version,
- scalability – Drupal has a flexible structure and can support even the largest and most complex multilingual websites.
Adding New Language and Configuring Translations
Adding New Language and Configuring Translations
This section will explain how to add new languages to your Drupal website and configure translations in the admin panel.
Translation Modules
Since version 8, there are a few built-in multilingual modules in Drupal:
- Language – basic module, necessary for every website that does not have English as the base language or uses a multilingual function,
- Content translation – allows for translating content,
- Configuration translation – translates the configuration in the admin panel,
- Interface translation – a language module responsible for translating the user interface.
Adding New Language
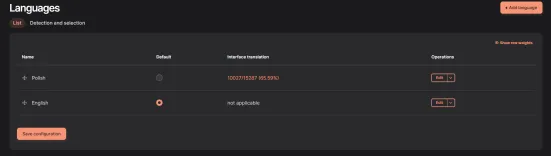
Go to Configuration -> Region and language -> Languages. You should see a list of previously installed languages:

Click Add language to add a new language:

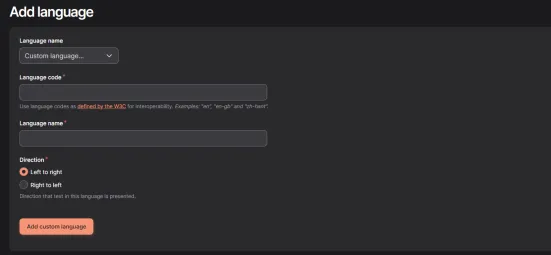
Select a language from the list and click Add language. If it’s not on the list, you can add it manually by selecting Custom language:

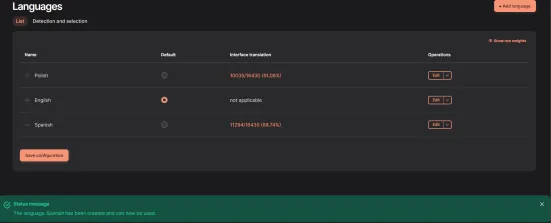
After clicking Add custom language, the translation starts downloading. Then you will be redirected to the installed languages list, where you will see the message:

Language Switcher
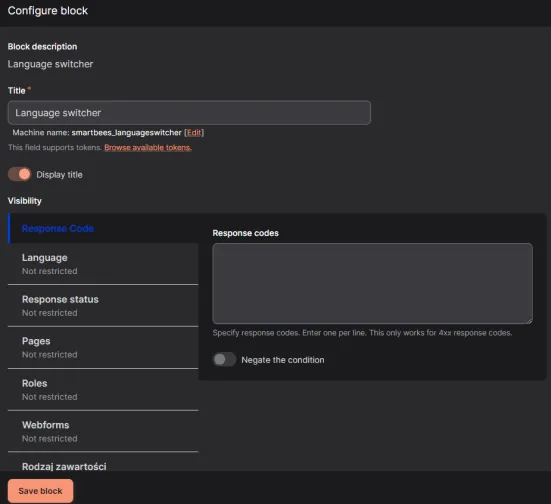
Now head to Structure -> Block layout. Click Place block and search for a new language switcher block:

Website Elements Configuration
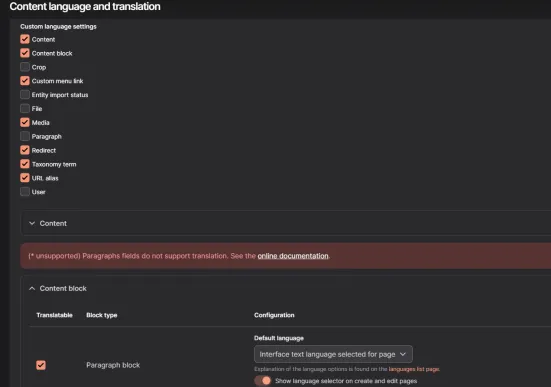
To translate page elements such as content types, taxonomy dictionaries, or user profiles, go to Configuration -> Region and language -> Content language and translation:

In Custom language settings, choose which sections should have more language options. Below are the settings for each section. Check the box next to them in the Translatable section.
Content Translation
Content Translation
Now that you have learned the process of adding a language and configuring translations in Drupal, let’s get down to content translation.
Create New Content or Edit an Existing Page
Go to the Content tab, then in the Operations section choose the Translate option.
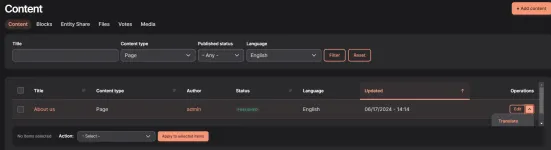
Select a Language
After clicking Translate, you will see a list of all the languages. Notice that the Spanish language we added has not yet been translated. Now click Add to create the translation.
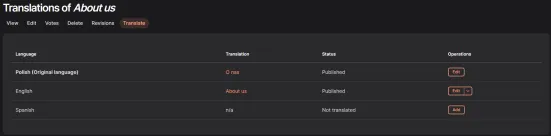
Add Translated Content to the Appropriate Fields
In the last step add translated content and save changes:
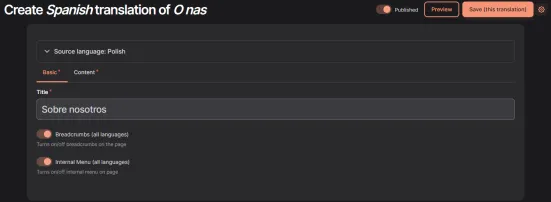
Configuration Translation
Configuration Translation
To translate the interface in the admin panel, head to Configuration -> Region and language -> Configuration translation.
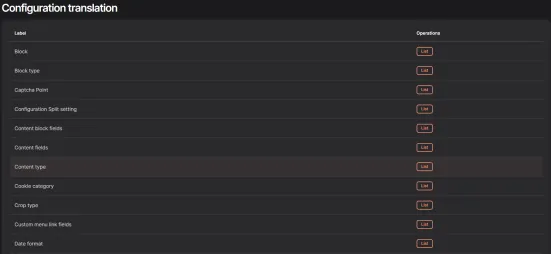
The list shows all the page configuration elements that can be translated. To translate a sample section, click the List button assigned to the section, and then select the element by clicking Translate.
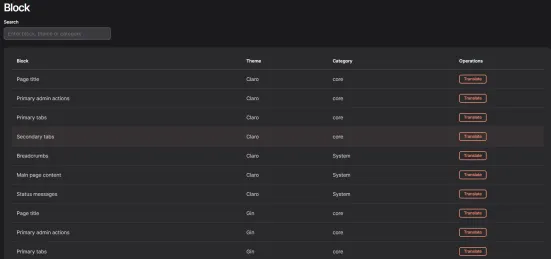
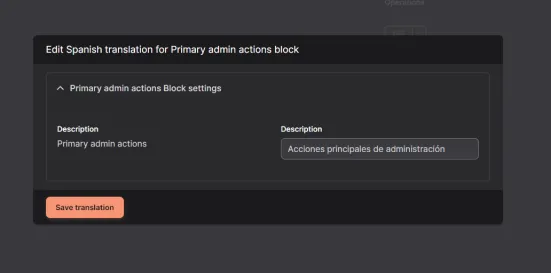
Now select the language in which you want to edit content, and then click Save translation.
SEO Optimization for Multilingual Sites
SEO Optimization for Multilingual Sites
SEO Optimization for a multilingual Drupal website requires considering different factors that can affect page visibility for different languages. Here are some key aspects to focus on.
URLs for Different Language Versions
Make sure your website’s URL structure is set up correctly for different language versions. Drupal offers URL configuration tools that allow you to create readable addresses for each language.
Meta Tags for Each Language
Ensuring you have correct meta tags, such as meta title, meta description and meta keywords for each language version can help improve your website’s visibility.
For multilingual sites, it is also worth implementing the “hreflang” attribute. It informs the search engine that the website has different versions for specific languages, which positively affects SEO. It is placed in the <head> section, in the <link> link.
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="pl" href=”https://xyz.com/pl/” />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href=”https://xyz.com” />
Creating Sitemaps for Different Language Versions
Create separate sitemaps for each language version and register them in webmaster tools such as Google Search Console. This will ensure easy indexing of all language versions.
Avoiding Content Duplication
Avoid duplicating content between different language versions, as this can negatively impact your search engine rankings. Follow canonicity rules and keep your content unique in each language version.
Monitoring and Analyzing the Results
Regularly monitor SEO results for different language versions using tools such as Google Analytics. Analyze data on organic traffic, conversion rates, and user behavior to adjust your optimization efforts.
Summary
Summary
Setting up a multilingual website in Drupal can be a challenge but with the right tools and procedures, you can do it effectively and efficiently. Alternatively, you can consult Drupal experts who will certainly help you.
In this article, we’ve covered the necessary steps to create a multilingual Drupal website, including installation, configuring languages, and managing content translations. Bear in mind that each website might have its own unique requirements, so tailor these tips to your specific goals and expectations.