How to Set Up and Use Workflows and Content Moderation Modules in Drupal?
Drupal’s default workflow doesn’t always meet user needs. When you have to review content before publishing, the Content Moderation module becomes a key tool. It allows you to define and control content workflows. Discover how the Content Moderation module can help you manage content in Drupal.

When Do You Need the Content Moderation Module?
When Do You Need the Content Moderation Module?
When you save content, Drupal creates a new, updated version. It then sets this as the default, which is retrieved when you load the entity using its ID.
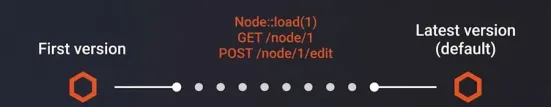
A problem arises when you don’t want to modify live content, or when you want to review a post before publishing changes.

In this case, you need a content moderation module that supports workflow management with states and transitions.
States
States

When editing content, such as a blog post, Drupal can keep the current version and create a new draft alongside it. Over time, this results in many revisions of the same post. While all copies are stored in the database, only one is visible on the site (or active).
This is similar to tracking changes in a Word document or viewing the history of a file in a version control system like Git.
1. Published Version
Drupal determines which content version to load when a page is visited. Therefore, the published version is marked as the default and displayed to visitors.
2. Pending Version
With the Content Moderation module, you can create a newer version than the published one. This is known as a pending version (draft).
3. Archived version
When a new default version is created, the previous one is archived. This allows you to treat past versions as history and the draft as a potential future version of the post.
The history of moderated content may look like this:

This allows for editing content without modifying the live version.
Workflow – What Is It?
Workflow – What Is It?
By default, Drupal provides a very simple content moderation workflow. Content is either published or unpublished. If you need more complex capabilities, the Workflows and Content Moderation modules come into play.
The Workflows module provides one or more workflows, defined as a set of states and transitions (i.e., moving content from one state to another).
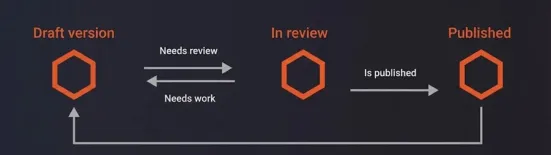
Each content type can have its own workflow or share it with another content type.

Planning the Workflow
Planning the Workflow
Drupal editorial workflow planning is often longer than the configuration itself. Start by defining roles for the people who interact with your website’s content. For example:
- authors – create content but may not have permission to publish;
- reviewers – review and publish content;
- technical reviewers – verify content from a technical perspective;
- administrators – usually have access to edit all content.
Prepare the Action Plan
Begin by creating a list of roles, states, and transitions you think will be needed. Then, consult representatives from each role to ensure the plan meets the needs of all involved parties.
The roles responsible for working with content are:
- Author,
- Technical reviewer,
- Copywriter,
- Publishing manager.
The states represent the current state of a particular revision. These are:
- Draft,
- Needs technical review,
- Needs editorial review,
- Scheduled for publication,
- Coming soon,
- Published.
This approach simplifies the Drupal content workflow and eliminates doubts about the stage of content preparation.
State transitions might look like this:

Some states, such as Needs technical review and Scheduled for publication, do not require editing, so the content remains unchanged. The technical reviewer can suggest corrections and send the draft back, but they do not make direct changes – that is the author's responsibility.
Other states, such as Needs editorial review, require editing. Therefore, you must ensure a new version is saved. When planning workflows, identify when a state change triggers a new revision.
Once the action plan is ready, you can start configuring the Workflows and Content Moderation modules.
Module Installation
Module Installation
Both modules are included in Drupal core – you can install them directly from the admin panel.
- Go to the Extend tab or /admin/modules;
- find the Drupal Content Moderation module on the list;
- enabling it requires the Workflows module. Click Continue to install both modules at once;
- you will be notified when the installation is complete.
Creating a Workflow
Creating a Workflow
It’s time to create your workflow.
- Go to Configuration→ Workflow→ Workflows or /admin/config/workflow/workflows. There you will find an overview of all workflows. By default, there’s one – Editorial.
- To add a new workflow, click + Add workflow, enter a label, and select the Content Moderation type. You will receive a confirmation notification.
When creating a new workflow, two states are automatically added: Draft and Published. There are also new transitions: Create new draft and Publish.
State Management
Editing the Drupal publishing workflow lets you add, modify, or delete states. On the edit page for each state, you can configure or delete transitions.
To add a new state, click Add a new state, then enter a name in the Label field. This will serve as an identifier for content administrators.
Pay attention to the two optional checkboxes that determine the behavior of the content in this state:
- Published – sets the item’s state to 'published' whenever the editor saves it in this mode. Otherwise, it remains unpublished.
- Default revision – sets this revision as the default. This informs the system which version to display when loading the entity.
After saving the new state, you will be redirected to the workflow configuration form. A success message will also appear. Repeat the process to add all the states you need.
Transition Management
As with states, editing the workflow allows you to create, modify, and delete transitions. You can change the transition name and select basic details.
To add a new transition, click Add new transition and enter a name in the Transition label field. Once the new transition is saved, you will be redirected to the workflow configuration page. A success message will appear, and the new transition will be listed at the bottom. Repeat this process to add more transitions.
Adding the Workflow to a Content Type
Adding the Workflow to a Content Type
To use the workflow with a specific content type, you need to assign it. Select the desired content type from the list and click Save.
When you assign the workflow to a content type with existing content, items will automatically be assigned the Draft or Published state, depending on their current publication status.
Setting Permissions
Setting Permissions
Workflows generate new, unique permissions for each transition. For example, the default Editorial workflow provides specific permissions. A transition allows you to change the content state. Any user with the required permission can perform this action. If you want to restrict permissions related to transitions:
- Create new user roles.
- Configure role permissions.
- Assign the role to the user.
Post Moderation
Post Moderation
With content moderation enabled, the publishing options at the bottom of the form change. The standard Published checkbox is replaced by a dropdown menu. This list includes all available moderation states.
Adding New Moderated Content
1. In the admin panel, go to Content → Add content.
2. After filling out the form, use the Save as dropdown to select the state. Click Save.
Editing Existing Content to Change the State
If you are logged in as a user with moderation permissions, you will see a control block allowing you to easily change the state of your content. The current state is displayed along with other metadata in the upper right corner.
Creating the Draft
1. Find the content you want to edit and click Edit. Alternatively, go to the admin panel and select Content. Click Edit next to the item on the list.
2. At the bottom of the form, find the Change to field and select Draft. Then click Save.
3. After saving the form, Drupal creates a new draft and leaves the default revision visible to visitors.
Managing Content Revisions
To publish a draft, go to the Latest version tab. Use the form to set the desired state, such as Published. Then click Apply. This will set the draft as the default revision, and the previous version will be archived. You can also manage Drupal content revisions in the Revisions tab. All revisions, except the current default, have an action button.
Additional Modules and Resources
Additional Modules and Resources
Here is a list of some modules worth checking out:
- Diff – allows you to view all added, changed, or deleted content between revisions.
- Content Moderation Notifications – allows you to receive email notifications when content changes state.
- Moderation dashboard – provides a dashboard in the user profile; includes useful blocks related to content management.
- Scheduler – allows you to schedule content publication for a specific time.
Summary
Summary
The Content Moderation module isn’t just a simple Drupal add-on – it’s a tool with enormous potential. It allows you to create advanced transitions between content states, tailored to individual user needs. With a wide range of options and constant updates from the Drupal community, this module is crucial for effective content management on your website.
Additionally, you can create your own modules, which opens the door to limitless options for customizing Drupal to your needs.
If you encounter any issues configuring the Content Moderation module, please refer to the module’s documentation.


