Enhancing Accessibility in Drupal: Top Modules and Tools for WCAG Compliance
Building accessible websites for people with disabilities should be a common practice nowadays. The Drupal CMS is helpful in this matter. How does it support creating webpages available for everyone? Find out from the following article.

Accessibility Features in CMS Systems
Accessibility Features in CMS Systems
People with various disabilities also use the Internet. However, some websites and apps are not well-aligned with their needs. It restricts disabled people from using them freely. This is the reason for developing international accessibility standards, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). It ensures equal access to information and features.
CMS systems offer built-in availability solutions and additional modules to install. Drupal is one of them. It contains embedded features that make WCAG easier to implement. This system also provides lots of extensions for existing mechanisms. Some of them even add new functions.
This article introduces key Drupal accessibility modules that improve the implementation of accessible websites. Learn how to install, configure, and use them. You will also discover their benefits.
Why Is Accessibility Important?
Why Is Accessibility Important?
People with any disability should not feel excluded from public life. Each website owner and developer ought to be ethically responsible for building accessible webpages. This approach contributes to including disabled people in society and guarantees equal access to digital resources and services.
Public entities must comply with digital accessibility standards; however, private ones are not obligated to obey them. Nonetheless, any business goes over better when its services and products are available to most users. WCAG standards implementation in private entities is not only a facilitation for people with specific dysfunctions. It is also an opportunity to gain potential customers.
WCAG 2.1 Accessibility in Drupal: Legal Aspects
WCAG 2.1 Accessibility in Drupal: Legal Aspects
Each country establishes its own accessibility regulations. However, many depend on international WCAG standards formed by the W3C.
Section 508 is part of the United States Rehabilitation Act. Its requirements cover providing easy access to all information and communication technologies, including websites, for people with disabilities and/or impairments. This regulation is closely aligned with WCAG 2.0 or 2.1 AA. If your website is available in the US, you must comply with these standards.
There are three regulations in the United Kingdom: Public Sector Bodies (Websites and Mobile Applications) Accessibility Regulations 2018, Equality Act 2010, and BS EN 301 549. Websites available in the UK are also obligated to be compliant with WCAG 2.1 AA.
The European Union’s directive 2016/2102 (EN 301 549) requires the member states’ public sector to share websites and apps that are compatible with WCAG 2.1. Another version, WCAG 2.2, has been available since October 2023. All of these regulations’ purpose is to ensure equal access to information and online services for everyone, regardless of ability.
Drupal as an Accessibility Support
Drupal as an Accessibility Support
Drupal CMS has been emphasizing accessibility for a long time. Here are a few examples of Drupal development features that simplify website creation:
Incorporated Accessibility Features
Built-in Drupal accessibility tools are integrated into every platform version, for instance, semantic HTML markup. It improves interoperability with assistive devices such as screen readers.
In addition, the system provides color contrasts and uses ARIA attributes, which are crucial for proper interface elements labelling. In every Drupal version, starting with the 7th, features such as form enhancements are being updated and expanded with new functions. Each one has to be up-to-date with the newest accessibility standards.
WCAG and ARIA Standards Compliance
Drupal allows adding ARIA to any content type and field. Core themes already have these inbuilt attributes. You will also not encounter any problems while creating new extensions from scratch. Use said attributes in essential sections such as headers, navigation, main content, and footer.
The Most Important Drupal Accessibility Extensions
The Most Important Drupal Accessibility Extensions
You can come across many Drupal modules that enhance the website’s accessibility. The most useful ones are listed below.
Editoria11y
Editoria11y is a tool that identifies potential issues with accessibility in Drupal by displaying relevant information on the website. It shows missing or poorly implemented features. With that being said, you can correct any errors before publishing the content.
How to configure and use this extension?
1. Install the module in the administration panel or use Drush.
2. Configure settings to enable scanning the content in editing mode. You can set which elements the extension should check for accessibility and which it should skip.
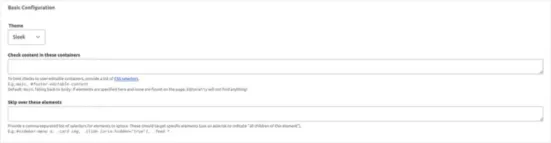
3. While editing content, the module delivers information about accessibility issues and possible solutions.

4. Grant proper permissions. You can distribute them between anonymous and authenticated users, content editors, and administrators. Be careful – some permissions are for security purposes and should only be given to trusted roles.
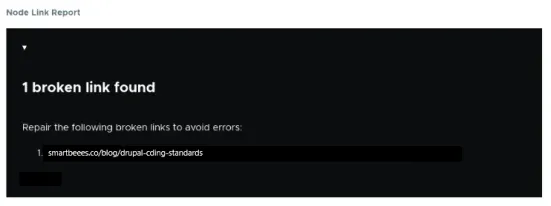
Node Link Report
The Node Link Report module aims to monitor broken links in Drupal. You will receive a notification about detecting a defective link, allowing you to fix it. This benefits not only the accessibility but also SEO.
Node Link Report configuration:
1. Install the module in Drupal’s administration panel or use Drush.
2. Choose the information block’s location.
3. View reports and fix broken links to improve navigation and website’s availability.
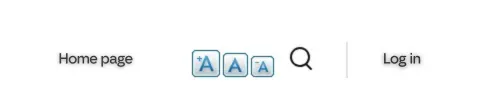
Text Resize
The Text Resize is a Drupal accessibility module designed for people with vision impairments. It enables font size adjustment without any browser settings changes.
Text Resize configuration
1. Install the module in Drupal – use the administration panel or Drush.
2. Configure the extension to add text resize tool. Select buttons location in block layout.
3. Ensure that the users can change text size with the available buttons.
Fluidproject UI Options
This Drupal accessibility module enables changes in font size and type, line spacing, contrast, and link style. Modifications made are saved using cookies.
How to install and configure Fluidproject UI Options?
1. Install the module using administration panel or Drush.
2. Decide which websites will display the extension.
3. This module enables modifications within font size and style, line spacing, and contrast.

Accessibility in Drupal Websites: Useful Tips
Accessibility in Drupal Websites: Useful Tips
There are a few key facets to consider when implementing WCAG on Drupal.
- Semantic HTML markups – use such HTML tags as header, nav, main, article, and aside. It will help assistive tools with recognizing site structure and simplifying the navigation.
- Regular tests – you can detect issues and fix them early on by checking the availability frequently.
- Keyboard navigation – many disabled people exploit their keyboards to use the web. Interactive elements’ accessibility is the key to well-adapted website. Tab order should be intuitive and logical. Ensure that using the mouse is not necessary.
- Alt text – images, videos and other multimedia should have alt text describing them. Also make sure there is transcription in the videos. This way people with hearing impairments will be able to understand the clue of the film.
- Color contrast – diversity between the text and the background is crucial for readability, especially for vision impaired people. It should be at level AA recording to WCAG 2.1 requirements. If the basic graphic design does not meet the demand, consider enabling a switch from the primary version to a contrasting one.
- Forms – legitimate box labeling, clear issue notifications and navigation between form areas provide digital accessibility.
These guidelines’ employment makes the website more user-friendly, especially for people with disabilities and impairments. They are highly recommended for both public and private entities.
Accessibility Testing – Tools and Techniques
The key to securing digital availability to as many users as possible is systematic testing. Manual tests are fundamental when it comes to WCAG; however, you can also use automated testing tools. The most popular methods are listed below:
- automated testing – use WAVE, axe or lighthouse to ensure meeting WCAG standards on the website. These tools provide detailed issue reports and suggest how to resolve the problem,
- manual tests – automatic testing tools are not able to fully analyze website’s accessibility even though they can catch a large amount of errors. That’s why the manual method is still useful. It includes navigating the site with a keyboard, assistive technologies such as screen readers, and browsing the code for correct HTML and ARIA semantics implementation,
- user tests – people with impairments and disabilities are the first to notice the website’s accessibility level. If there is a chance of obtaining their help, it is worth considering. In this case, assistive devices’ user is more perceptive than any testing feature.
Common Errors
Here are the most frequent mistakes in accessibility implementation:
- Skipping alt text for images and other multimedia.
- Incorrect form errors handling.
- Flawed contrast usage.
- Complicated and inconclusive labelling.
- Dynamic content overload without suitable ARIA descriptions.
If you avoid these common mistakes, your website will be well-adapted to everyone.
Summary
Summary
Providing availability is one of the website development essentials, regardless of the CMS system used. Various built-in tools and modules can provide high-quality accessibility in Drupal and enable website creation in compliance with WCAG standards.
Digital availability implementation means more than just module configuration. It includes numerous tests in terms of convenience for disabled people. This should be a part of the development process. The more errors you detect during site building or modification, the more polished your site will be in production.